The master cylinder is a critical component of a vehicle’s braking system, responsible for converting mechanical force from the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure that activates the brakes. Choosing the best master cylinder brake system depends on several factors, including vehicle type, braking requirements, and budget. A high-quality master cylinder ensures reliable and responsive braking performance, which is crucial for vehicle safety.
When selecting a master cylinder, it’s important to consider factors such as bore size, material quality, and compatibility with your vehicle’s braking system. The right master cylinder can significantly improve braking efficiency, pedal feel, and overall safety. Let’s explore the key aspects of master cylinder brake systems to help you determine which option is best for your needs.
| Factor | Importance |
|---|---|
| Bore Size | Affects braking force and pedal travel |
| Material | Influences durability and heat resistance |
| Compatibility | Ensures proper fit and function |
| Brand Reputation | Indicates reliability and quality |
Types of Master Cylinder Brake Systems
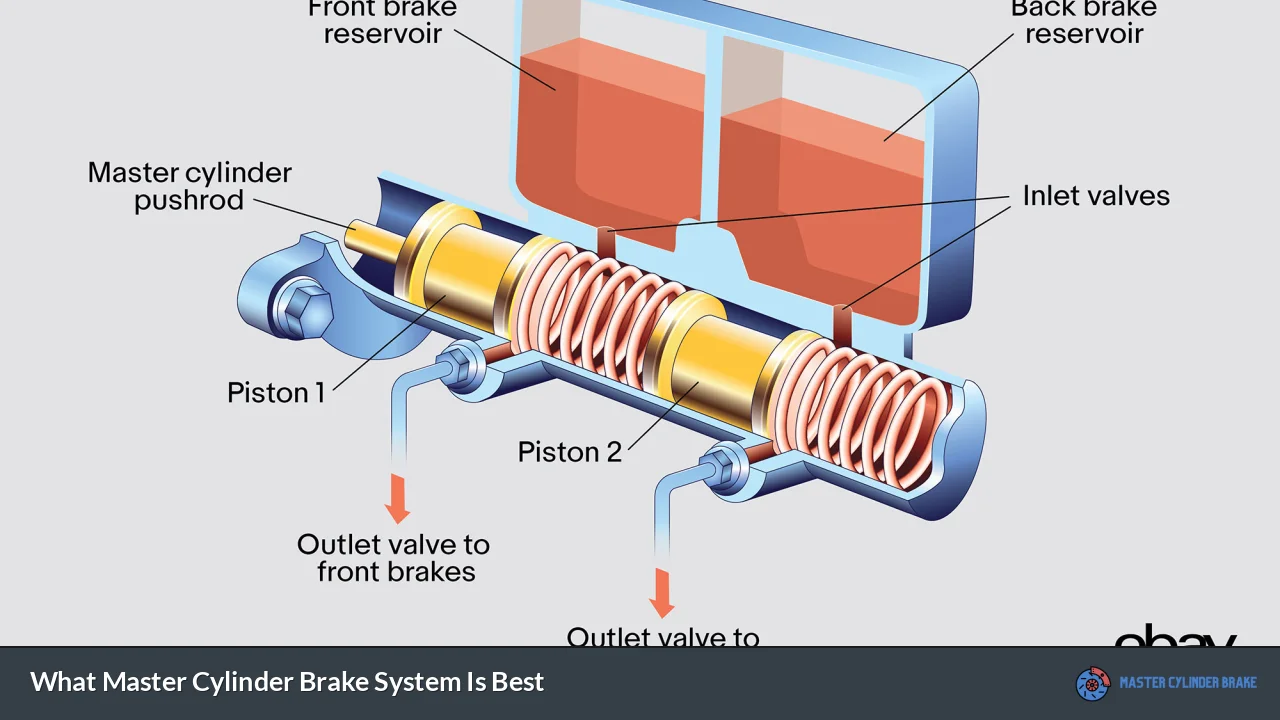
There are several types of master cylinder brake systems available, each with its own advantages and ideal applications. The two main categories are single circuit and dual circuit master cylinders.
Single circuit master cylinders are the simplest design, with one piston controlling the brake fluid for all wheels. While these were common in older vehicles, they are rarely used in modern cars due to safety concerns. If a leak occurs in a single circuit system, it can result in complete brake failure.
Dual circuit master cylinders are the standard in modern vehicles. They feature two separate circuits, each controlling a pair of wheels. This design provides a crucial safety feature: if one circuit fails, the other can still provide some braking power. Dual circuit systems typically use one of three configurations:
- Front/Rear Split: One circuit controls the front brakes, while the other controls the rear brakes.
- Diagonal Split: Each circuit controls one front wheel and the opposite rear wheel.
- Four-Wheel Split: Both circuits control all four wheels, with one circuit taking over if the other fails.
The choice between these configurations depends on the vehicle’s weight distribution, intended use, and manufacturer preferences. Diagonal split systems are particularly common in passenger vehicles as they provide balanced braking even if one circuit fails.
Another important distinction in master cylinder design is between fixed bore and stepped bore cylinders. Fixed bore cylinders have a consistent diameter throughout, while stepped bore cylinders have different diameters for the primary and secondary pistons. Stepped bore designs can provide more balanced braking force distribution between the front and rear brakes.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Master Cylinder
Selecting the best master cylinder brake system requires careful consideration of several factors:
1. Bore Size: The bore diameter affects the amount of fluid displaced and the pedal effort required. A larger bore generally provides more braking power but may require more pedal force.
2. Material: Master cylinders are typically made from cast iron, aluminum, or plastic. Cast iron is durable but heavy, aluminum offers a good balance of strength and weight, while plastic is lightweight but may not be as durable for high-performance applications.
3. Compatibility: Ensure the master cylinder is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year. It should also match your brake system’s requirements, including the number of wheels, brake type (disc or drum), and ABS compatibility.
4. Pedal Ratio: This refers to the mechanical advantage provided by the brake pedal. A higher pedal ratio reduces the effort needed to apply the brakes but may increase pedal travel.
5. Reservoir Capacity: Adequate fluid capacity is crucial for maintaining proper brake function, especially in high-performance or heavy-duty applications.
6. Brand Reputation: Opt for well-known brands with a history of producing reliable brake components. Some reputable manufacturers include Brembo, Wilwood, Bosch, and ATE.
7. Intended Use: Consider whether the vehicle is for daily driving, performance driving, or heavy-duty applications. Each scenario may require different master cylinder specifications.
Top Master Cylinder Brake Systems
While the “best” master cylinder can vary depending on specific needs, here are some highly regarded options:
1. Wilwood Tandem Chamber Master Cylinder: Known for its high-quality construction and versatility, this master cylinder is popular in performance and racing applications.
2. Brembo Racing Master Cylinder: Offers exceptional performance and precise brake modulation, ideal for high-performance vehicles and motorsports.
3. Bosch Brake Master Cylinder: Provides reliable performance for a wide range of vehicles, known for its durability and OEM-quality fit.
4. ATE Original Brake Master Cylinder: Offers excellent quality and performance for European vehicles, known for its precision engineering.
5. Centric Premium Brake Master Cylinder: Provides a good balance of quality and affordability, suitable for many domestic and import vehicles.
These options are generally considered top-tier, but the best choice for your vehicle will depend on its specific requirements and your braking needs.
Installation and Maintenance
Proper installation and maintenance of your master cylinder are crucial for optimal performance and safety. Here are some key points to consider:
- Professional Installation: Unless you have significant automotive experience, it’s recommended to have a professional mechanic install your new master cylinder. Improper installation can lead to brake failure.
- Brake Fluid: Use the correct type of brake fluid as specified by your vehicle manufacturer. Mixing different types of brake fluid can cause system damage.
- Bleeding the System: After installation, the brake system must be properly bled to remove any air bubbles. Air in the system can cause spongy brake feel and reduced braking efficiency.
- Regular Inspections: Periodically check for leaks, proper fluid level, and any signs of wear or damage.
- Fluid Replacement: Brake fluid absorbs moisture over time, which can lead to corrosion and reduced performance. Follow your vehicle manufacturer’s recommendations for fluid replacement intervals.
By choosing the right master cylinder brake system and maintaining it properly, you can ensure optimal braking performance and safety for your vehicle.
FAQs About Master Cylinder Brake Systems
- How often should a master cylinder be replaced?
Master cylinders typically last 60,000-100,000 miles, but replacement may be needed sooner if leaks or performance issues occur. - Can I upgrade my master cylinder for better performance?
Yes, upgrading to a higher-quality or larger bore master cylinder can improve braking performance, especially for modified vehicles. - What are signs of a failing master cylinder?
Common signs include a sinking brake pedal, uneven braking, brake fluid leaks, and warning lights on the dashboard. - Is it necessary to replace both the master cylinder and brake booster together?
Not always, but if one component fails, it’s often recommended to replace both for optimal performance and compatibility. - Can I use a universal master cylinder in my vehicle?
While universal options exist, it’s best to use a master cylinder specifically designed for your vehicle to ensure proper fit and function.